Ever heard of interleaved practice and wonder how and why it works? Here’s how you can use the strategy of interleaved practices to enhance your learning and performance. Read on to discover a few tips, backed by research!
Table of Contents:
- Comparing Interleaved vs Blocked Practice
- Research Study on Interleaved Practice
- Some Personal Examples on Interleaving Concepts
- Concluding Remarks
Comparing Interleaved vs Blocked Practice
Conventionally, we learn by utilising primarily blocked practice, which refers to a strong emphasis on an individual topic through repetition until an adequate & desirable proficiency has been obtained, before moving on to another topic. However, with the advent of more integrated approaches in curriculum throughout education (problem-based learning, case-based learning, etc.), the concept of interleaved practice has been much more widely discussed and researched about.
What is interleaved practice?
Interleaved practice involves alternating between different skills or topics during learning sessions.
In summary, here is a list of pros & cons of the two based on some research articles/studies I have read & my personal experience:
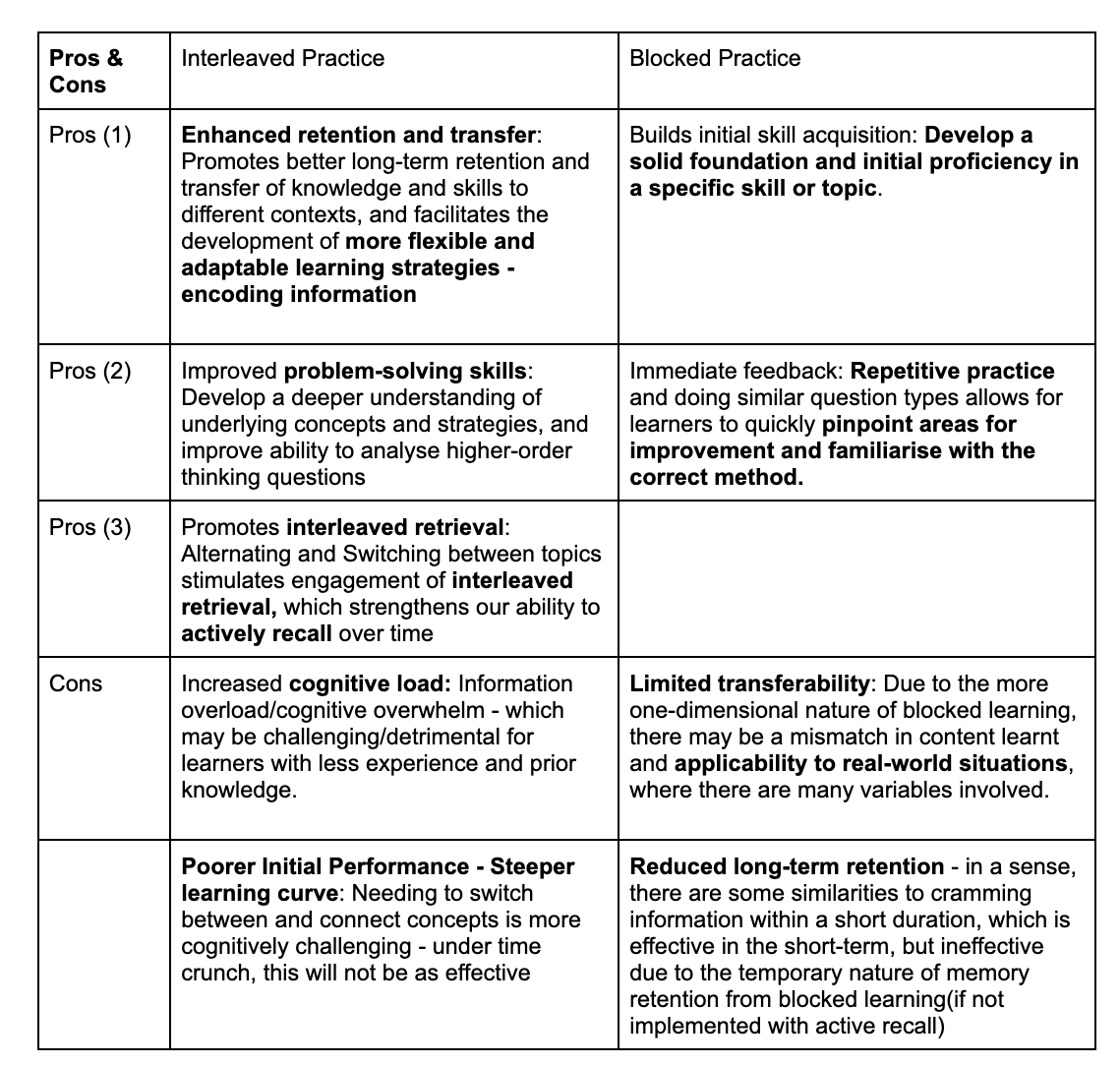
Adapted from:
- Schneider, V. I., & Bjork, R. A. (2018). Memory for medical information: A comparison of different practice schedules. Memory, 26(1), 118-128. doi: 10.1080/09658211.2017.1347749
- Rohrer, D., & Taylor, K. (2007). The shuffling of mathematics problems improves learning. Instructional Science, 35(6), 481-498. doi: 10.1007/s11251-007-9015-8
- Kang, S. H. K., & Pashler, H. (2012). Learning painting styles: Spacing is advantageous when it promotes discriminative contrast. Applied Cognitive Psychology, 26(1), 97-103. doi: 10.1002/acp.1817
Research Study on Interleaved Practice
Curious to find out more, I chanced upon a research study conducted in an undergraduate physics class in the United States, which compared the use of blocked practice (isolating individual concepts) and interleaving practices over a period of time. Assignments utilising interleaved practice questions were found to be more challenging than conventional homework (in topical/chronological order), but the group of students who committed to completing the interleaved practices demonstrated higher scores in both recall test and learning assessments, indicating an improvement in learning outcomes.
The findings suggest that interleaved practice is an effective learning strategy for undergraduate physics students. Interleaving different topics during study sessions helps consolidate learning and improves long-term memory retention. Additionally, interleaved practice enhances problem-solving skills by promoting the transfer of knowledge across different topics, leading to improved problem-solving abilities. However, some slight drawbacks could be noted, regarding the greater cognitive demand on students due to the higher-order critical thinking skills required to be able to connect between as well as differentiate between different concepts.
Adapted from:Samani J, Pan SC. Interleaved practice enhances memory and problem-solving ability in undergraduate physics. NPJ Sci Learn. 2021 Nov 12;6(1):32. doi: 10.1038/s41539-021-00110-x. PMID: 34772951; PMCID: PMC8589969.
Personal Examples on Interleaving Concepts
This also brought me back to how when I was learning about biological concepts, I liked to combine topics when consolidating so that when revising one topic, I will be able to draw connections to other topics seamlessly – and to utilise diverse learning techniques to aid my learning (Mnemonics, Analogies, Mind Maps).
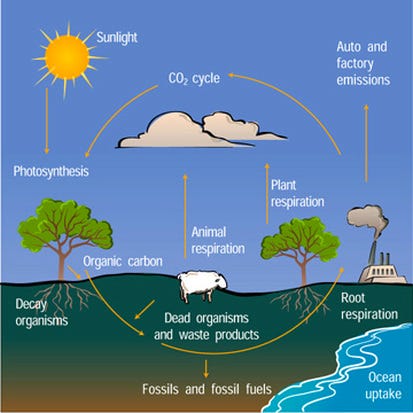
Source: Mrs. McComas, CC BY-SA 4.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
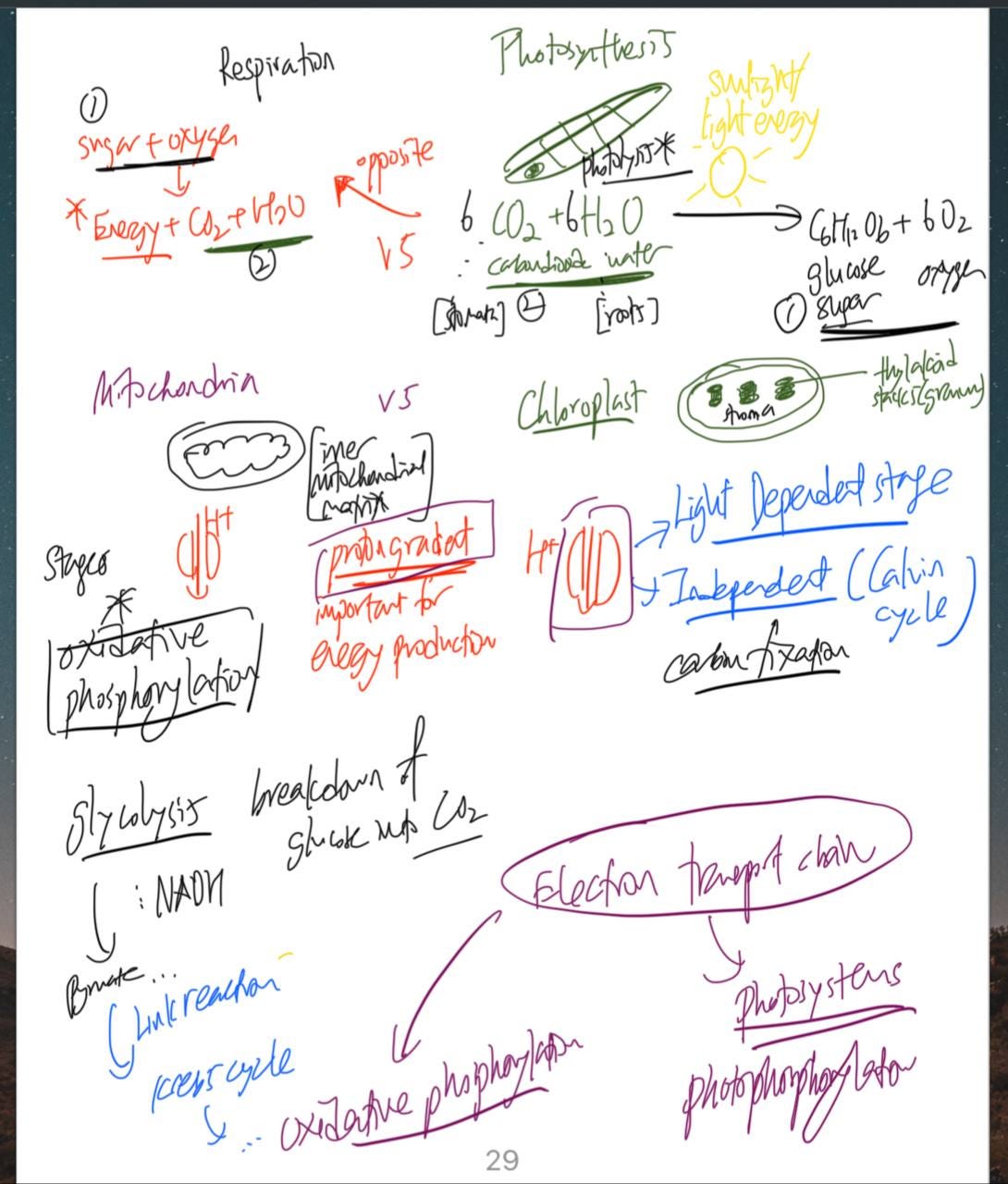
For example, when learning about aerobic + anaerobic respiration as well as photosynthesis on a cellular level, it helped to draw parallels as well as identify contrasting ideas between respiration & photosynthesis (Difference between overall reaction of these two processes, location of processes – across thylakoid/mitochondrial membrane, similarities and differences between the use of electron transport chain & proton gradient, etc.) – Pardon my poor handwriting and messy annotations :p
How this can relate to interleaved practices is that we can be more mindful of retrieving information from different sources & concepts when revising, which also allows us to craft more thought-provoking questions that compare and analyse differing ideas, helping us gain a clearer picture and ability to distinguish between them. (This is something that I will attempt in the near future with ChatGPT as well, perhaps you guys could try it out as well!)
This concept is something that is also commonly used in Mathematics, even at a primary school level, where Algebra, Fraction, Ratio, Percentage, Models – are used interchangeably to analyse proportions & solve questions, requiring a need to differentiate and also integrate these different topics together.
An example of a possible question I created for my primary 6 student(combining Ratio & Percentage)

Concluding Remarks
Indubitably, it is important to have a good foundation and fundamental understanding of the different topics at hand to be able to effectively apply and connect the dots. However, being able to consistently utilise interleaved practices with spaced repetition will likely result in a greater depth of understanding that is much harder to achieve with blocked practice alone, especially if it is a concept that you wish to gain a stronger mastery in.
Therefore, I think it will be beneficial to utilise different modes of learning (blocked AND interleaved) and experiment with them to fit your own custom learning style, and discover what is most effective for you.
Happy Reading~
Check out some of my other articles on learning:
